The PMO book provides a comprehensive overview of Project Management Offices (PMOs) and their role within organizations. The book covers various aspects related to PMOs, including their definition, importance, and different types such as Project PMO, Program PMO, Portfolio PMO, and Center of Excellence.
The book further explores the structures and characteristics of PMOs, discussing their challenges and benefits. It delves into the PMO project life cycle and provides guidance on setting up a PMO, starting from identifying the need for a PMO to developing a PMO charter and securing executive support.
Additionally, the book outlines the functions and responsibilities of PMOs, covering areas such as project governance, portfolio management, resource management, risk management, quality management, and communication management. It also highlights the various tools and techniques utilized by PMOs, including project management methodologies, software, and reporting and analytics tools.
The book emphasizes best practices for PMOs, such as aligning projects with business strategy, standardizing project management processes, providing training and support to project managers, and fostering continual improvement and innovation. It also addresses measuring PMO performance through key performance indicators (KPIs), PMO maturity models, and benefits realization management.
The factors essential for PMO success are discussed, and case studies are presented to showcase successful PMO implementations as well as lessons learned from PMO failures. The book concludes by exploring the future of PMOs, including their role in agile and digital transformation and driving business innovation.
In summary, this PMO book provides a comprehensive and informative guide to understanding the concepts, functions, and importance of PMOs in organizations, serving as a valuable resource for PMO practitioners, project managers, and individuals interested in project management and organizational effectiveness.
Definition of PMO
The Project Management Office (PMO) is a department or group within an organization that defines and maintains standards for project management. The PMO strives to standardize and introduce economies of repetition in the execution of projects, ensuring all projects are conducted consistently and efficiently.
The PMO is the source of documentation, guidance, and metrics related
to the practices involved in managing and implementing projects within
the organization. It can also oversee the selection, management, and
execution of projects, ensuring they align with the organization's
strategic objectives and goals.
The PMO can exist at different levels in an organization, from
overseeing specific projects or portfolios to setting project management
policy at an enterprise level. The specific roles and responsibilities
of a PMO can vary widely, depending on the structure and needs of the
organization it serves.
The Role and Importance of PMO in an Organization
Standardization: The PMO establishes standardized project
management processes, methodologies, and templates to ensure consistency
across all projects. This helps in reducing confusion, improving
efficiency, and increasing the quality of project delivery.
Strategic Alignment: The PMO ensures that all projects align
with the strategic goals and objectives of the organization. It helps in
prioritizing projects based on their strategic value, ensuring that
resources are allocated to the most important initiatives
Governance: The PMO provides a framework for project governance,
defining roles and responsibilities, decision-making processes, and
escalation procedures. This helps in ensuring accountability and
effective decision-making.
Resource Management: The PMO manages resources across projects,
ensuring that they are effectively allocated and utilized. It helps in
avoiding resource conflicts and ensuring that projects have the
necessary resources to succeed.
Risk Management: The PMO identifies, assesses, and manages
project risks, helping to prevent issues that could derail projects. It
ensures that risks are proactively managed and mitigated.
Training and Support: The PMO provides training and support to
project managers and teams, helping to improve their skills and
capabilities. It also promotes the sharing of knowledge and best
practices across the organization
Performance Tracking and Reporting: The PMO tracks and reports
on project performance, providing critical information to stakeholders
and senior management. It helps in identifying issues early, enabling
corrective action to be taken.
The PMO, therefore, plays a vital role in improving project success
rates, enhancing project management maturity, and increasing the value
that projects deliver to the organization.
↚
Types of PMOs
Project PMO
A Project PMO, or Project Management Office, is a type of PMO that operates at the project level within an organization. Its primary role is to support a specific project with project management tools, methodologies, and resources.
The Project PMO is typically responsible for:
Project Planning: This includes defining project objectives,
scope, and deliverables, developing the project schedule, and
identifying required resources.
Project Execution: The Project PMO oversees the execution of
project tasks, ensuring they are completed on time and within
budget.
Quality Management: The Project PMO ensures that project
deliverables meet the required quality standards.
Risk Management: The Project PMO identifies potential project
risks and develops strategies to mitigate them.
Communication: The Project PMO facilitates communication among
project stakeholders, ensuring everyone is informed about project
progress, issues, and changes.
Documentation: The Project PMO is responsible for maintaining
project documentation, including project plans, status reports, and
lessons learned.
The Project PMO is typically disbanded once the project is completed.
However, the lessons learned and best practices identified by the
Project PMO can be used to improve project management processes for
future projects.
Program PMO
A Program PMO, or Program Management Office, is a type of PMO that oversees and coordinates a group of related projects that together achieve a common goal or objective. These related projects constitute a program.
The Program PMO is typically responsible for:
Program Planning: This includes defining the program's
objectives, scope, and deliverables, developing the program schedule,
and identifying required resources across all projects within the
program.
Program Governance: The Program PMO establishes and maintains
the program governance structure, including decision-making processes,
roles and responsibilities, and escalation procedures.
Coordination: The Program PMO coordinates the execution of
individual projects within the program, ensuring they are aligned and
integrated to achieve the program's objectives.
Risk and Issue Management: The Program PMO identifies and
manages risks and issues at the program level, which may impact multiple
projects within the program.
Benefits Management: The Program PMO tracks and manages the realization
of benefits from the program, ensuring that the program delivers the
expected value to the organization.
Stakeholder Communication: The Program PMO facilitates
communication among program stakeholders, ensuring everyone is informed
about program progress, issues, and changes.
Documentation: The Program PMO is responsible for maintaining
program documentation, including program plans, status reports, and
lessons learned
The Program PMO plays a crucial role in ensuring that the individual
projects within a program are coordinated and managed in a way that
maximizes the overall benefits to the organization.
Portfolio PMO
A Portfolio PMO, or Portfolio Management Office, is a type of PMO that oversees and manages a portfolio of projects and programs. A portfolio is a collection of projects, programs, subsidiary portfolios, and operations managed as a group to achieve strategic objectives.
The Portfolio PMO is typically responsible for:
Portfolio Strategy Alignment: The Portfolio PMO ensures that all projects and programs within the portfolio align with the strategic goals and objectives of the organization. It helps in prioritizing projects and programs based on their strategic value.
Governance: The Portfolio PMO establishes and maintains the portfolio governance structure, including decision-making processes, roles and responsibilities, and escalation procedures.
Resource Management: The Portfolio PMO manages resources across
all projects and programs within the portfolio, ensuring that they are
effectively allocated and utilized.
Risk Management: The Portfolio PMO identifies and manages risks
at the portfolio level, which may impact multiple projects or programs
within the portfolio.
Performance Management: The Portfolio PMO tracks and manages the
performance of the portfolio, ensuring that the portfolio delivers the
expected value to the organization.
Stakeholder Communication: The Portfolio PMO facilitates
communication among portfolio stakeholders, ensuring everyone is
informed about portfolio progress, issues, and changes.
Documentation: The Portfolio PMO is responsible for maintaining
portfolio documentation, including portfolio plans, status reports, and
lessons learned.
The Portfolio PMO plays a crucial role in ensuring that the
organization's project investments are aligned with its strategic
objectives and are delivering the expected value. It provides a holistic
view of the organization's project landscape, enabling better
decision-making and resource allocation.
Center of Excellence
A Center of Excellence (Coed) is a team, a shared facility or an entity
that provides leadership, best practices, research, support and/or
training for a focus area. The focus area might be a technology (like
data science), a business concept (like project management), a skill
(like negotiation), or a broad area of study (like women's health).
In the context of project management, a PMO Center of Excellence refers
to a centralized unit within an organization that is responsible for
promoting excellence in project management. It does this by:
Developing and Maintaining Standards: The Coed develops and
maintains project management standards, methodologies, and best
practices. It ensures that these are consistently applied across all
projects.
Training and Development: The Coe provides training and
development opportunities for project managers and project teams. This
helps to improve their skills and capabilities.
Knowledge Sharing: The Coes promotes the sharing of knowledge
and lessons learned across the organization. This helps to improve
project management practices and outcomes.
Resource Management: The CoE may also be involved in managing
project resources, ensuring that they are effectively allocated and
utilized.
Strategic Alignment: The CoE ensures that all projects align
with the strategic goals and objectives of the organization.
Performance Measurement: The CoE measures and reports on project
performance, providing critical information to stakeholders and senior
management.
By promoting best practices and continuous improvement in project
management, the PMO Center of Excellence helps to increase project
success rates, improve efficiency, and enhance the organization's
ability to deliver on its strategic goals.
↚
PMO Structures and Their Characteristics
PMO stands for Project Management Office. It is a centralized
department or function within an organization that is responsible for
overseeing and managing project-related activities. PMOs can have
different structures and characteristics, depending on the
organization's needs and objectives. Here are some common PMO structures
and their characteristics.
Supportive PMO: This type of PMO provides support and guidance
to project managers and teams. It offers templates, tools, and best
practices to ensure consistency and efficiency in project management
processes.
Controlling PMO: A controlling PMO focuses on enforcing project
management standards and procedures. It ensures compliance with
organizational policies and monitors project performance through regular
reporting and audits.
Directive PMO: In a directive PMO, project managers are assigned
by the PMO, and they have limited autonomy. The PMO controls project
decisions and manages resources, making it a more centralized and
hierarchical structure.
Hybrid PMO: A hybrid PMO combines elements from different
structures to meet specific organizational needs. It may provide
support, control, and guidance based on the project's nature, size, and
complexity.
Enterprise PMO: An enterprise PMO oversees all projects and
programs within an organization. It aligns project portfolios with
strategic objectives, facilitates resource allocation, and provides
overall governance.
Characteristics of PMOs can include:
Standardized project management processes and methodologies.
Clear roles and responsibilities for project managers and teams.
Resource management and allocation.
Risk management and mitigation strategies.
Monitoring and reporting project progress.
Providing training and development opportunities for project
managers.
Continuous improvement and lessons learned.
Collaboration and knowledge sharing across projects.
It's important to note that PMOs can vary in their level of authority,
influence, and scope of responsibilities, depending on the
organization's size, industry, and project management maturity.
↚
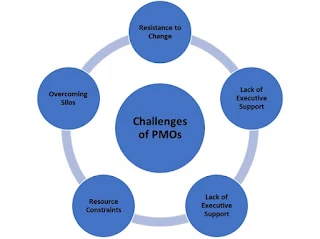
Challenges of PMOs
PMOs face several challenges, including:
Resistance to Change: Implementing a PMO may face resistance
from individuals or teams accustomed to existing project management
approaches.
Lack of Executive Support: Without strong support from top
management, PMOs may struggle to gain authority and influence within the
organization.
Resource Constraints: Limited resources, such as budget, staff,
or technology, can pose challenges to the effective functioning of a
PMO.
Lack of Alignment: PMOs may face difficulties in aligning
project portfolios with strategic objectives and ensuring consistent
decision-making across projects.
Overcoming Silos: Breaking down silos and fostering
collaboration among different departments or business units can be a
challenge for PMOs.
↚
Benefits of PMOs
PMOs (Project Management Offices) offer several benefits,
including:
Standardization and Consistency: PMOs establish standardized
project management processes, methodologies, and templates, ensuring
consistency and efficiency across projects.
Improved Project Success Rates: PMOs provide guidance, support,
and oversight, increasing the likelihood of project success through
better planning, monitoring, and risk management.
Enhanced Resource Management: PMOs help optimize resource
allocation, ensuring that the right resources are available for projects
and avoiding resource conflicts.
Increased Visibility and Reporting: PMOs provide regular
reporting and performance metrics, enabling stakeholders to have a clear
view of project progress, risks, and outcomes.
Knowledge Sharing and Lessons Learned: PMOs facilitate knowledge
sharing, best practices, and lessons learned, fostering continuous
improvement and organizational learning.
Strategic Alignment: PMOs align project portfolios with
strategic objectives, ensuring that projects contribute to the
organization's overall goals and priorities.
Improved Decision-Making: PMOs provide data-driven insights and
analysis, enabling informed decision-making at both project and
organizational levels.
It's important to note that the specific challenges and benefits of a
PMO can vary depending on the organization's context, culture, and
industry. A well-designed and effectively implemented PMO can address
challenges and deliver significant benefits to an organization's project
management capabilities.
↚
PMO Project Life Cycle
The PMO Life Cycle refers to the stages a Project Management Office (PMO) goes through from its inception to its maturity. It typically includes the following phases: Initiating, Planning, Implementation, and Improvement.
PMO Initiating: This is the first phase of the PMO Life Cycle.
It involves defining the purpose and objectives of the PMO, identifying
stakeholders, and securing executive sponsorship. The PMO's role and
responsibilities are clearly defined, and a preliminary PMO charter is
developed. This phase also involves assessing the organization's current
project management capabilities and identifying the need for a PMO.
PMO Planning: In this phase, a detailed plan for setting up the
PMO is developed. This includes defining the PMO's structure, roles and
responsibilities, processes, and tools. The PMO's key performance
indicators (KPIs) are also defined in this phase. The planning phase
also involves developing a communication plan to inform stakeholders
about the PMO and its benefits.
PMO Implementation: This phase involves setting up the PMO
according to the plan. This includes recruiting and training the PMO
team, implementing the PMO processes and tools, and launching the PMO.
The PMO starts to take on project management responsibilities, such as
overseeing projects, providing support to project teams, and reporting
on project performance.
PMO Improvement: This is the final phase of the PMO Life Cycle.
It involves continuously monitoring the PMO's performance, collecting
feedback from stakeholders, and making improvements. This could involve
refining the PMO's processes and tools, providing additional training to
the PMO team, or expanding the PMO's responsibilities. The goal is to
continuously enhance the PMO's effectiveness and value to the
organization.
Each phase of the PMO Life Cycle is crucial for establishing a
successful PMO that can effectively support project management and
contribute to the organization's strategic objectives.
↚
Setting Up a PMO
Identifying the Need for a PMO
Identifying the need for a Project Management Office (PMO) within an organization often stems from recognizing certain challenges or opportunities. Here are some indicators that a PMO might be beneficial.
Lack of Standardization: If projects are managed inconsistently,
with different methodologies and processes, it can lead to confusion,
inefficiency, and poor-quality outcomes. A PMO can provide standardized
project management practices.
Poor Project Performance: If projects frequently run over
budget, miss deadlines, or fail to meet their objectives, a PMO can help
improve project planning, execution, and control.
Strategic Misalignment: If projects are not aligned with the
organization's strategic objectives, a PMO can ensure that project
selection and prioritization are tied to strategic goals.
Resource Conflicts: If there are frequent conflicts over
resources, or if resources are under- or over-utilized, a PMO can
provide effective resource management.
Inadequate Risk Management: If projects often encounter
unanticipated problems, a PMO can help implement systematic risk
management processes.
Lack of Visibility: If senior management does not have a clear
view of project performance, a PMO can provide regular, standardized
reporting.
Need for Improved Communication: If there's a lack of effective
communication among project stakeholders, a PMO can facilitate better
communication and collaboration.
Need for Project Management Training: If project managers or
team members lack necessary project management skills, a PMO can provide
training and support.
By addressing these issues, a PMO can help improve project success
rates, increase efficiency, and enhance the organization's ability to
achieve its strategic objectives.
Defining the PMO's Scope and Objectives
Defining the scope and objectives of a Project Management Office (PMO)
is a critical step in its establishment. This process involves clearly
outlining what the PMO will do (its scope) and what it aims to achieve
(its objectives). Here's how you might go about defining these.
↚
Scope of the PMO
The scope of the PMO refers to the range of its activities and responsibilities. This could include:
Project Support: Providing tools, templates, and best practices
to project teams.
Project Management: Directly managing certain projects or
programs.
Training and Development: Offering training and development
opportunities for project managers and teams.
Governance: Establishing project governance structures and
processes.
Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that projects align with the
organization's strategic objectives.
Resource Management: Managing resources across projects.
Risk Management: Identifying and managing project risks.
Performance Reporting: Tracking and reporting on project
performance.
↚
Objectives of the PMO
The objectives of the PMO are the specific outcomes that it aims to achieve. These could include:
Improve Project Success Rates: Increase the percentage of
projects that are delivered on time, within budget, and to the
satisfaction of stakeholders.
Standardize Project Management Practices: Implement consistent
project management methodologies and processes across all projects.
Enhance Strategic Alignment: Improve the alignment of projects
with the organization's strategic objectives.
Optimize Resource Utilization: Ensure that resources are
effectively allocated and utilized across projects.
Mitigate Project Risks: Reduce the impact and likelihood of
project risks.
Increase Project Management Maturity: Improve the organization's
project management capabilities and maturity.
Enhance Stakeholder Satisfaction: Increase the satisfaction of
project stakeholders, including project teams, sponsors, and
customers.
Defining the scope and objectives of the PMO provides a clear direction
for its activities and helps to ensure that it delivers value to the
organization.
↚
Securing Executive Support
Securing executive support is crucial for the success of a Project Management Office (PMO) for several reasons.
Authority: Executive support gives the PMO the authority it
needs to enforce project management standards and processes across the
organization. Without this authority, the PMO may struggle to get
project teams to adhere to its methodologies.
Resources: Executives control the allocation of resources within
the organization. Their support can ensure that the PMO has the
necessary resources, including staff, budget, and tools, to perform its
functions effectively.
Change Management: The establishment of a PMO often involves
significant changes to how projects are managed. Executives can play a
key role in managing this change, helping to overcome resistance and
ensure buy-in from project teams and other stakeholders.
Strategic Alignment: The PMO needs to ensure that projects align
with the organization's strategic objectives. Executives can provide the
strategic direction and insights needed to achieve this alignment.
Visibility and Credibility: Executive support can increase the
visibility and credibility of the PMO within the organization. This can
help the PMO to gain the trust and cooperation of project teams and
other stakeholders.
Problem Solving: Executives can assist in resolving issues that
are beyond the control of the PMO, such as conflicts between projects or
departments.
For these reasons, securing executive support should be a key priority
when establishing a PMO.
Developing a PMO Charter
Developing a PMO Charter is a critical step in establishing a Project Management Office (PMO). The charter serves as a formal document that outlines the purpose, scope, and objectives of the PMO, as well as its roles, responsibilities, and governance structure. Here are the steps to develop a PMO Charter.
Define the Purpose: Clearly state why the PMO is being
established. This could be to improve project success rates, standardize
project management practices, or enhance strategic alignment, among
other reasons.
Outline the Scope: Describe the range of activities and
responsibilities of the PMO. This could include project support, project
management, training and development, governance, strategic alignment,
resource management, risk management, and performance reporting.
Set the Objectives: Specify what the PMO aims to achieve. These
objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and
time-bound (SMART).
Identify Roles and Responsibilities: Define who will be part of
the PMO and what their roles and responsibilities will be. This could
include the PMO director, project managers, project support staff, and
other roles.
Establish the Governance Structure: Describe how the PMO will be
governed. This could include the decision-making processes, escalation
procedures, and reporting lines.
Specify the Methodologies and Tools: Identify the project
management methodologies and tools that the PMO will use. This could
include specific project management frameworks, software, and
templates.
Plan for Resource Requirements: Estimate the resources that the
PMO will need, including staff, budget, and tools.
Define Success Measures: Determine how the success of the PMO
will be measured. This could include specific key performance indicators
(KPIs) or other metrics.
Get Approval: Once the PMO Charter has been developed, it should
be presented to the relevant stakeholders for approval. This typically
includes senior management and other key stakeholders.
The PMO Charter serves as a foundational document for the PMO,
providing a clear direction for its activities and a basis for its
accountability. It should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure it
remains relevant and effective.
↚
PMO Functions and Responsibilities
Project Governance
Project governance is indeed one of the key functions and responsibilities of a Project Management Office (PMO). It refers to the framework for how project decisions are made and who makes them. It provides a structured process for decision-making and ensures accountability, transparency, and effective management of project risks and resources. Here's how the PMO contributes to project governance.
Establishing Governance Framework: The PMO develops and
implements a governance framework that outlines the processes, roles,
and responsibilities for decision-making in projects. This includes
defining who has the authority to make decisions at different stages of
the project, and the process for escalating decisions when needed.
Setting Standards and Procedures: The PMO sets standards and
procedures for project management, including project initiation,
planning, execution, control, and closure. These standards ensure
consistency and quality in the way projects are managed.
Ensuring Compliance: The PMO ensures that all projects comply
with the established governance framework and project management
standards. This includes conducting audits or reviews to check for
compliance.
Risk Management: The PMO identifies and manages project risks,
ensuring that they are appropriately mitigated and that there is a plan
in place to respond to any issues that arise.
Decision-Making Support: The PMO supports effective
decision-making by providing accurate and timely information to project
stakeholders. This includes project status reports, risk assessments,
and performance metrics.
Stakeholder Management: The PMO manages project stakeholders,
ensuring that they are engaged and informed, and that their interests
are taken into account in decision-making.
By providing a framework for project governance, the PMO helps to
ensure that projects are managed in a controlled, consistent, and
effective manner, increasing the likelihood of project success.
Project Portfolio Management
Project Portfolio Management (PPM) is indeed a key function and responsibility of a Project Management Office (PMO). PPM involves managing and optimizing a portfolio of projects to achieve strategic objectives. Here's how the PMO contributes to PPM.
Strategic Alignment: The PMO ensures that all projects within
the portfolio align with the organization's strategic objectives. It
helps in prioritizing projects based on their strategic value and
potential return on investment.
Portfolio Optimization: The PMO balances the portfolio to
achieve the right mix of projects. This involves considering factors
such as risk, reward, cost, resource availability, and interdependencies
between projects.
Resource Allocation: The PMO manages the allocation of resources
across the portfolio, ensuring that each project has the necessary
resources to succeed and that resources are used efficiently.
Performance Management: The PMO tracks and manages the
performance of the portfolio, ensuring that the portfolio as a whole is
delivering the expected value to the organization. This includes
monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and taking corrective
action when necessary.
Risk Management: The PMO identifies and manages risks at the
portfolio level, which may impact multiple projects within the
portfolio. It ensures that risks are proactively managed and
mitigated.
Governance: The PMO provides a governance structure for the
portfolio, defining roles and responsibilities, decision-making
processes, and escalation procedures.
Communication: The PMO facilitates communication among portfolio
stakeholders, ensuring everyone is informed about portfolio progress,
issues, and changes.
By managing the project portfolio, the PMO helps to ensure that the
organization's project investments are aligned with its strategic
objectives and are delivering the expected value. It provides a holistic
view of the organization's project landscape, enabling better
decision-making and resource allocation.
Resource Management
Resource Management is indeed a key function and responsibility of a Project Management Office (PMO). It involves planning, allocating, and managing the resources needed to complete a project. These resources can include human resources (project team members), as well as financial resources, equipment, and technology. Here's how the PMO contributes to resource management.
Resource Planning: The PMO helps in identifying what resources
are needed for each project, including the number of team members, their
roles and skills, and any necessary equipment or technology.
Resource Allocation: The PMO is responsible for allocating
resources to projects based on their needs and priorities. This involves
balancing the demands of multiple projects and ensuring that resources
are used efficiently.
Resource Scheduling: The PMO schedules resources for project
tasks, taking into account the availability of resources and the
timeline of the project.
Resource Utilization: The PMO monitors the utilization of
resources, ensuring that they are being used effectively and
efficiently. If resources are under- or over-utilized, the PMO can make
adjustments as necessary.
Resource Forecasting: The PMO forecasts future resource needs
based on the project pipeline and strategic plans. This helps the
organization to plan ahead and ensure that sufficient resources will be
available when needed.
Conflict Resolution: The PMO helps to resolve resource
conflicts, such as when two projects need the same resources at the same
time. This can involve negotiating with project managers, re-scheduling
tasks, or finding alternative resources.
By managing resources effectively, the PMO helps to ensure that
projects have the resources they need to succeed, and that resources are
used efficiently and effectively across the organization.
Risk Management
Risk Management is indeed a crucial function and responsibility of a Project Management Office (PMO). It involves the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks that could potentially impact the successful completion of a project. Here's how the PMO contributes to risk management.
Risk Identification: The PMO helps in identifying potential
risks that could affect the project. This involves a thorough
understanding of the project, its environment, and potential factors
that could lead to uncertainty.
Risk Assessment: Once risks are identified, the PMO assesses
them in terms of their potential impact and the likelihood of their
occurrence. This helps in prioritizing risks and focusing on those that
could have the greatest impact on the project.
Risk Mitigation: The PMO develops strategies to mitigate the
identified risks. This could involve avoiding the risk, reducing the
impact or likelihood of the risk, transferring the risk to another
party, or accepting the risk and developing a contingency plan.
Risk Monitoring: The PMO continuously monitors and reviews risks
throughout the life of the project. If new risks emerge, or if the
impact or likelihood of existing risks changes, the PMO adjusts the risk
management plan accordingly.
Communication: The PMO communicates about risks with project
stakeholders. This ensures that everyone is aware of the risks and the
steps being taken to manage them.
Risk Reporting: The PMO reports on risks to senior management
and other stakeholders. This includes providing information on the
overall risk profile of the project, as well as specific risks and their
status.
By managing risks effectively, the PMO helps to increase the likelihood
of project success, reduce uncertainty, and enhance decision-making.
Quality Management
Quality Management is indeed one of the key functions and responsibilities of a Project Management Office (PMO). It involves ensuring that the project's deliverables meet the required standards and expectations. This is achieved through various processes and techniques, including quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control.
Quality Planning: This involves identifying the quality
requirements and standards for the project and its deliverables, and
documenting how the project will demonstrate compliance with these
requirements.
Quality Assurance: This is the process of auditing the quality
requirements and the results from quality control measurements to ensure
that appropriate quality standards and operational definitions are
used.
Quality Control: This involves monitoring and recording results
of executing the quality activities to assess performance and recommend
necessary changes.
The PMO is responsible for setting up the quality management processes,
ensuring they are followed, and continuously improving them. It also
ensures that all project stakeholders understand the quality objectives
and are working towards them. The PMO may also be involved in training
team members on quality management techniques and tools.
In essence, the PMO plays a crucial role in ensuring that the
project's deliverables are of high quality, meet the stakeholders'
expectations, and comply with the necessary standards and
regulations.
Communication Management
Communication Management is indeed one of the key functions and responsibilities of a Project Management Office (PMO). It involves the systematic planning, implementing, monitoring, and revision of all the channels of communication within an organization, and between organizations.
Here's a more detailed explanation
Planning: The PMO is responsible for developing a communication
plan that details who needs what information, when they need it and how
that information will be delivered. This includes identifying the
stakeholders, understanding their information needs and defining the
methods and frequency of communication.
Implementing: Once the plan is in place, the PMO ensures that
the communication happens as per the plan. This could involve arranging
meetings, sending out newsletters, updating project dashboards, etc.
Monitoring: The PMO also monitors the effectiveness of the
communication. This could involve gathering feedback from the
stakeholders, analyzing communication data and making necessary
adjustments to the communication plan.
Revision: As the project progresses, the communication needs may
change. The PMO is responsible for revising the communication plan as
needed and ensuring that everyone is kept informed about the project
status.
In essence, effective communication management ensures that all
stakeholders have a clear understanding of the project status, issues,
risks and achievements. This helps in managing expectations, improving
decision making and increasing stakeholder satisfaction.
↚
PMO Tools and Techniques
Project Management Methodologies
Project Management Methodologies are a set of principles or practices used by project management offices (PMOs) to guide project teams throughout the project lifecycle. They are considered as one of the essential tools and techniques used by PMOs to ensure successful project delivery.
There are several types of project management methodologies, each with
its own unique approach to managing project activities. Here are a few
examples.
Waterfall Methodology: This is a traditional project management
methodology that involves a linear project flow. Each phase of the
project must be completed before the next one begins, with no
overlapping or iterative steps.
Agile Methodology: This methodology is iterative and flexible.
It allows for changes and adjustments throughout the project lifecycle.
Agile methodology is often used in software development projects where
requirements and solutions evolve through the collaborative effort of
self-organizing and cross-functional teams.
Scrum: This is a type of Agile methodology that is used for
managing complex software and product development. It encourages team
collaboration and allows for quick problem-solving.
Lean: This methodology focuses on reducing waste and improving
efficiency. It aims to deliver more value to customers with fewer
resources.
Kanban: This is a visual approach to project management. It
helps teams manage their work and see the state of every piece of work
at any time.
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments): This is a
process-based method that focuses on organization and control over the
entire project, from start to finish.
The choice of methodology depends on the nature of the project, the
team's expertise, the business environment, and the specific
requirements of the client or stakeholder. The right methodology can
help a PMO manage resources more effectively, control costs, reduce
risks, and ultimately deliver successful projects.
Project Management Software
Project Management Software is a type of application that helps project managers (PMs) and their teams manage projects efficiently. It's considered a crucial tool in the Project Management Office (PMO) toolkit. This software provides a structured approach to planning, organizing, and managing resources to bring about the successful completion of specific project goals and objectives.
Here are some key features and benefits of Project Management
Software.
Task Management: It allows PMs to assign tasks to team members,
track progress, and manage dependencies between tasks.
Scheduling: It provides tools for creating project schedules,
setting deadlines, and managing timelines. Gantt charts are a common
feature for visualizing project timelines.
Collaboration: It offers platforms for team members to
communicate and collaborate on tasks. This can include shared calendars,
discussion boards, and file-sharing capabilities.
Document Management: It provides a centralized location for
storing and managing all project-related documents. This ensures that
all team members have access to the latest versions of documents.
Resource Allocation: It helps in tracking resources (both human
and material), ensuring they are effectively utilized and not
overbooked.
Risk Management: It provides tools for identifying, assessing,
and managing risks to the project.
Reporting: It offers a variety of reporting tools that can
provide insights into project performance and progress.
Examples of project management software include Microsoft Project,
Basecamp, Asana, Trello, and Jira. The choice of software often depends
on the specific needs and budget of the project team. By using project
management software, PMOs can increase efficiency, improve
communication, reduce risks, and deliver projects on time and within
budget
Reporting and Analytics Tools
Reporting and Analytics Tools are essential components of the Project Management Office (PMO) toolkit. They provide valuable insights into project performance and progress, enabling project managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions.
Here are some key features and benefits of Reporting and Analytics
Tools.
Data Collection and Integration: These tools can gather data
from various sources, such as project management software, financial
systems, and other business applications. This allows for a
comprehensive view of project data.
Data Visualization: They provide visual representations of data,
such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. This makes it easier to
understand complex data and identify trends or patterns.
Performance Tracking: They allow for tracking of key performance
indicators (KPIs), such as project completion rates, budget adherence,
and resource utilization. This helps in assessing the health and success
of projects.
Predictive Analytics: Some advanced tools use predictive
analytics to forecast future project outcomes based on historical data.
This can help in proactive decision-making and risk management.
Real-Time Reporting: They provide real-time updates on project
status, enabling quick responses to any issues or changes in the
project.
Customizable Reports: They allow for customization of reports to
meet the specific needs of different stakeholders.
Examples of Reporting and Analytics Tools include Tableau, Microsoft
Power BI, Google Analytics, and Zoho Analytics. By using these tools,
PMOs can ensure transparency, improve project control, enhance
decision-making, and ultimately increase the likelihood of project
success.
↚
PMO Best Practices
Aligning Projects with Business
Aligning projects with business strategy is a best practice for Project Management Offices (PMOs) This means that every project undertaken should support the strategic objectives of the business. This alignment ensures that resources are not wasted on projects that do not contribute to the overall goals of the organization.
Here's how this practice works
Understanding the Business Strategy: The first step is for the
PMO to have a clear understanding of the organization's business
strategy. This includes the organization's mission, vision, strategic
objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Project Selection: The PMO should ensure that only projects that
align with the business strategy are selected for execution. This can be
done using a project selection method such as scoring models, benefit
contribution, or financial analysis.
Strategic Planning: The PMO should be involved in strategic
planning to ensure that projects are designed to support strategic
objectives. This includes setting project goals that align with business
goals, and planning project activities that will contribute to achieving
these goals.
Performance Measurement: The PMO should measure project
performance in terms of contribution to strategic objectives. This
involves tracking KPIs that are linked to business goals, and reporting
on how projects are contributing to these goals.
Continuous Alignment: The PMO should ensure continuous alignment
of projects with business strategy. This involves regularly reviewing
and adjusting projects as necessary to ensure they remain aligned with
changing business strategies.
By aligning projects with business strategy, PMOs can ensure that
projects deliver maximum value, contribute to business success, and
enhance the organization's competitive position.
Standardizing Project Management Processes Strategy
Standardizing project management processes is a best practice for Project Management Offices (PMOs). This involves creating a common set of practices, templates, and rules to be used across all projects in the organization. The goal is to ensure consistency, improve efficiency, and increase the quality of project delivery.
Here's how this practice works
Process Development: The PMO develops standardized processes for all
stages of the project lifecycle, from initiation and planning to
execution, monitoring, and closure. These processes are based on best
practices in project management and are tailored to the needs of the
organization.
Templates and Tools: The PMO creates templates for project
documents such as project plans, status reports, and risk registers. It
also provides tools for project scheduling, budgeting, and risk
management. These templates and tools ensure consistency and save time
by eliminating the need to start from scratch for each project.
Training and Support: The PMO provides training to project
managers and team members on the standardized processes, templates, and
tools. It also provides ongoing support to help them apply these
standards in their projects.
Compliance Monitoring: The PMO monitors projects to ensure
compliance with the standardized processes. This can involve regular
audits or reviews of projects.
Continuous Improvement: The PMO regularly reviews and updates
the standardized processes based on feedback from project teams and
lessons learned from completed projects. This ensures that the processes
remain effective and relevant.
By standardizing project management processes, PMOs can reduce
variability, improve predictability, and increase the success rate of
projects. It also makes it easier to manage multiple projects at the
same time and facilitates knowledge sharing and learning across
projects.
Providing Training and Support to Project Managers
Providing training and support to project managers is indeed a best practice for Project Management Offices (PMOs). This practice is crucial for enhancing the skills and competencies of project managers, ensuring they are equipped to effectively manage projects and lead their teams
Here's how this practice works
Training Programs: The PMO organizes regular training programs
to educate project managers about the latest project management
methodologies, tools, and best practices. This could include training on
specific project management software, risk management techniques, or
leadership skills.
Mentorship and Coaching: The PMO can provide one-on-one
mentorship or coaching to project managers, especially those who are new
or less experienced. This can help them navigate challenges, learn from
experienced professionals, and develop their skills.
Knowledge Sharing: The PMO can facilitate knowledge sharing
sessions where project managers can learn from each other's experiences,
share insights, and discuss common challenges. This can foster a culture
of continuous learning and improvement.
Resource Provision: The PMO provides project managers with the
resources they need to manage their projects effectively. This could
include project management software, templates, guidelines, or access to
expert advice.
Support and Guidance: The PMO offers ongoing support and
guidance to project managers throughout the project lifecycle. This
could involve helping with project planning, monitoring project
progress, resolving issues, or providing advice on decision-making.
By providing training and support, PMOs can ensure that project
managers are well-prepared to deliver successful projects. This can lead
to improved project performance, higher project success rates, and
increased satisfaction among project stakeholders.
Continual Improvement and Innovation
Continual Improvement and Innovation is a best practice for Project Management Offices (PMOs). This involves constantly seeking ways to improve project management processes, tools, and techniques, and fostering a culture of innovation to enhance project outcomes.
Here's how this practice works:
Feedback and Lessons Learned: The PMO collects feedback from
project teams and stakeholders, and conducts "lessons learned" sessions
at the end of each project. This information is used to identify areas
for improvement and develop action plans.
Process Improvement: The PMO regularly reviews and updates
project management processes to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
This could involve streamlining workflows, automating tasks, or
introducing new methodologies.
Innovation: The PMO encourages project teams to come up with innovative
solutions to project challenges. This could involve using new
technologies, experimenting with different approaches, or thinking
creatively to solve problems.
Training and Development: The PMO provides training and development
opportunities to enhance the skills and knowledge of project teams. This
could involve training on new tools or techniques, or workshops on
creative problem-solving.
Performance Measurement: The PMO tracks performance metrics to monitor
the effectiveness of improvement and innovation initiatives. This data
is used to make informed decisions and guide future improvement
efforts.
Change Management: The PMO manages the implementation of improvements
and innovations, ensuring that changes are smoothly integrated into
existing processes and that all stakeholders are on board
By focusing on continual improvement and innovation, PMOs can ensure
that their project management practices remain up-to-date and effective,
leading to improved project performance and success rates. This approach
also helps to create a dynamic and adaptable project management
environment that can respond effectively to changing circumstances
↚
Measuring PMO Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring PMO performance is crucial to ensure that it is effectively supporting project delivery and contributing to the organization's strategic objectives. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are used to measure the success and effectiveness of the PMO. Here are some common KPIs used to measure PMO performance.
Project Success Rate: This measures the percentage of projects
that are completed on time, within budget, and meet their objectives. A
high success rate indicates effective project management.
Project ROI (Return on Investment): This measures the financial
benefits derived from projects relative to their cost. A positive ROI
indicates that projects are delivering value for the organization.
Resource Utilization: These measures how effectively resources
(both human and material) are being used in projects. High resource
utilization indicates efficient use of resources.
Stakeholder Satisfaction: This measures the satisfaction of
project stakeholders, including project teams, clients, and senior
management. High stakeholder satisfaction indicates that the PMO is
effectively meeting the needs and expectations of stakeholders.
Project Delivery Time: This measures the average time taken to
deliver projects. Shorter delivery times can indicate more efficient
project management.
Budget Adherence: This measures how closely actual project costs
align with budgeted costs. High budget adherence indicates effective
budget management.
Quality Metrics: These measure the quality of project
deliverables, such as the number of defects or rework required.
High-quality metrics indicate effective quality management.
Risk Management: This measures the effectiveness of risk
management, such as the number of identified risks that were effectively
mitigated.
These KPIs provide a quantitative measure of PMO performance and can
help identify areas for improvement. It's important to choose KPIs that
align with the PMO's objectives and the organization's strategic
goals.
↚
PMO Maturity Models
PMO Maturity Models are tools used to assess the level of maturity of a Project Management Office (PMO). They help in understanding the current capabilities of the PMO and identifying areas for improvement. These models typically define different levels of maturity, with each level representing an increased ability to manage projects effectively and consistently.
Here are some common PMO Maturity Models and how they can be used to
measure PMO performance.
PMI's Organizational Project Management Maturity Model (OPM3):
This model assesses maturity in terms of project, program, and portfolio
management. It identifies capabilities in these areas and provides a
path for improvement
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI): Originally
developed for software development processes, CMMI can also be applied
to project management. It defines five levels of maturity, from initial
(chaotic, ad hoc, individual heroics) to optimizing (continuous process
improvement is enabled by quantitative feedback and from piloting
innovative ideas and technologies).
Portfolio, Programme, and Project Management Maturity Model
(P3M3):
This model assesses maturity across three dimensions: portfolio
management, program management, and project management. It defines five
levels of maturity, from level 1 (awareness of process) to level 5
(optimized process).
Kerzner Project Management Maturity Model (KPMMM): This model
focuses on the maturity of project management processes. It defines five
levels of maturity, from initial recognition of project management
through to continuous improvement.
Using these models, a PMO can conduct a self-assessment or engage
external consultants to perform an assessment. The results can provide
valuable insights into the PMO's strengths and weaknesses, and guide the
development of a roadmap for improvement. It's important to remember
that the goal is not just to achieve a higher level of maturity, but to
improve the PMO's ability to support the successful delivery of projects
that contribute to the organization's strategic objectives.
Benefits Realization Management
Benefits Realization Management (BRM) is a powerful way to measure the performance of a Project Management Office (PMO). It focuses on ensuring that projects deliver the expected benefits and contribute to the strategic objectives of the organization.
Here's how BRM can be used to measure PMO performance.
Identify Expected Benefits: At the start of each project, the
PMO should work with stakeholders to identify the expected benefits.
These benefits should be clearly defined, measurable, and aligned with
the organization's strategic objectives.
Plan for Benefits Realization: The PMO should develop a benefits
realization plan for each project. This plan should outline how and when
the benefits will be delivered, who will be responsible for delivering
them, and how they will be measured.
Track and Measure Benefits: Throughout the project lifecycle,
the PMO should track and measure the actual benefits delivered. This
involves collecting data on key performance indicators (KPIs) that are
linked to the expected benefits.
Evaluate and Report on Benefits Realization: At the end of the
project, the PMO should evaluate whether the expected benefits have been
realized. This involves comparing the actual benefits with the expected
benefits, and reporting on the results.
Continuous Improvement: The PMO should use the results of
benefits realization management to identify areas for improvement and
make adjustments to future projects. This can help to increase the
success rate of projects and improve the PMO's performance.
By focusing on benefits realization, PMOs can ensure that projects
deliver real value to the organization. This can enhance the credibility
of the PMO and demonstrate its contribution to the organization's
success.
↚
Key Factors for PMO Success
Clear Mandate and Support: A PMO should have a clear mandate and
support from top management. This includes having a defined scope,
authority, and resources to carry out its responsibilities
effectively.
Alignment with Organizational Strategy: The PMO should align its
activities and project portfolios with the strategic objectives of the
organization. This ensures that projects are contributing to the overall
goals and priorities of the organization.
Effective Governance and Decision-Making: A successful PMO
establishes governance structures and decision-making processes that
enable efficient and informed project oversight. This includes defining
roles and responsibilities, establishing clear communication channels,
and ensuring accountability.
Standardized Processes and Methodologies: Implementing
standardized project management processes and methodologies helps drive
consistency and efficiency across projects. This includes providing
templates, tools, and guidelines to project managers and teams.
Competent and Skilled Staff: Having a team of competent and
skilled professionals within the PMO is crucial for its success. This
includes project management expertise, as well as skills in areas such
as communication, leadership, and stakeholder management.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication: The PMO should
actively engage with stakeholders, including project managers, teams,
executives, and other relevant parties. Effective communication ensures
that expectations are managed, risks are addressed, and project progress
is transparent.
Continuous Improvement and Learning: A successful PMO promotes a
culture of continuous improvement and learning. This involves capturing
lessons learned from projects, implementing feedback mechanisms, and
adapting processes based on best practices and industry trends
Measurable Performance Metrics: Establishing performance metrics
and key performance indicators (KPIs) allows the PMO to track and
measure its effectiveness. This includes metrics related to project
success rates, resource utilization, stakeholder satisfaction, and other
relevant factors.
Flexibility and Adaptability: A successful PMO should be
flexible and adaptable to changing business needs and project
requirements. This includes being open to new methodologies,
technologies, and approaches that can enhance project management
practices.
Demonstrated Value and Benefits: Ultimately, a successful PMO
should be able to demonstrate its value and the benefits it brings to
the organization. This can be achieved through improved project
outcomes, increased efficiency, cost savings, and other tangible and
intangible benefits.
By focusing on these key factors, organizations can increase the
likelihood of PMO success and maximize the value they derive from their
project management capabilities.
↚
Case Studies
Successful PMO Implementations
Here are a few examples of successful PMO implementations.
Cisco Systems: Cisco Systems, a multinational technology
conglomerate, implemented a PMO to manage its numerous, complex
projects. The PMO helped standardize project management practices across
the organization, leading to improved project performance. The PMO also
played a key role in strategic planning, helping to align projects with
business objectives.
IBM: IBM, a multinational technology and consulting company,
established a PMO to improve the success rate of its projects. The PMO
implemented a standardized project management methodology, provided
training and support to project managers, and introduced a project
management software tool. As a result, IBM saw a significant increase in
project success rates and a reduction in project overruns.
British Airways: British Airways, a major airline, set up a PMO
to manage a large-scale business transformation project. The PMO
provided a structured approach to managing the project, with clear roles
and responsibilities, standardized processes, and regular progress
reporting. The project was successfully completed on time and within
budget, leading to significant business benefits.
U.S. Department of Energy: The U.S. Department of Energy
established a PMO to manage a portfolio of projects aimed at improving
energy efficiency. The PMO used a portfolio management approach to
prioritize projects based on their strategic importance and potential
benefits. This led to more effective use of resources and greater impact
from the projects.
These case studies demonstrate the value that a PMO can bring to an
organization, including improved project performance, better alignment
of projects with business strategy, and more effective use of
resources.
Lessons Learned from PMO Failures
While PMOs can bring significant benefits, they can also face challenges and failures. Here are some lessons learned from PMO failures.
Lack of Executive Support: PMOs need strong support from senior
management to be successful. Without this support, they may struggle to
enforce project management standards and gain cooperation from project
teams. Lesson: Secure executive buy-in and support from the start.
Misalignment with Business Strategy: If a PMO's goals and
projects are not aligned with the organization's business strategy, it
can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities. Lesson: Ensure
that the PMO's objectives and projects are closely aligned with the
business strategy.
Inadequate Resources: PMOs need sufficient resources, including staff, budget, and tools, to perform their functions effectively. Without these resources, they may struggle to deliver value.
Lesson: Ensure adequate resourcing for the PMO.
Lack of Skills and Training: If the PMO team lacks the necessary
project management skills and training, it can lead to poor project
performance. Lesson: Invest in training and development for the PMO
team.
Resistance to Change: Implementing a PMO often involves
significant changes to project management practices, which can meet
resistance from project teams. Lesson: Manage change effectively,
involving stakeholders in the process and communicating the benefits of
the PMO.
Failure to Demonstrate Value: If the PMO does not clearly
demonstrate its value, it can be seen as a bureaucratic overhead rather
than a valuable asset. Lesson: Regularly measure and communicate the
value that the PMO brings to the organization.
One Size Does Not Fit All: Implementing a PMO model or
methodology without considering the specific context and needs of the
organization can lead to poor fit and ineffective practices. Lesson:
Tailor the PMO to the specific needs and context of the
organization.
By learning from these failures, organizations can increase the chances
of PMO success and maximize the benefits that PMOs can bring.
↚
The Future of PMOs
The Impact of Agile and Digital Transformation on PMOs
The rise of Agile methodologies and digital transformation is having a significant impact on Project Management Offices (PMOs), and this trend is expected to continue in the future. Here are some key impacts.
Shift to Agile Methodologies: As organizations increasingly
adopt Agile methodologies, PMOs need to adapt their processes and tools
to support Agile projects. This can involve a shift from a
control-oriented approach to a more facilitative role, helping project
teams to apply Agile principles and practices.
Increased Speed and Flexibility: Digital transformation often
involves rapid changes and the need for quick decision-making. PMOs need
to become more flexible and responsive, able to quickly adjust project
plans and priorities to meet changing needs.
Focus on Value Delivery: With the customer-centric focus of
digital transformation, PMOs need to ensure that projects deliver real
value to customers. This can involve a greater focus on benefits
realization and measuring project success in terms of customer
outcomes.
New Skills and Competencies: The move to Agile and digital
transformation requires new skills and competencies, such as Agile
project management, digital technology skills, and change management.
PMOs need to ensure that project managers and teams have these skills,
through training and development initiatives.
Use of Digital Tools: Digital transformation brings new digital
tools for project management, such as cloud-based project management
software, collaboration tools, and data analytics. PMOs need to embrace
these tools to improve project management efficiency and
effectiveness.
Cultural Change: Agile and digital transformation often involve
a significant cultural change, towards a more collaborative, innovative,
and risk-tolerant culture. PMOs can play a key role in driving this
cultural change, by promoting Agile values and principles, and fostering
a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
In conclusion, Agile and digital transformation present both
challenges and opportunities for PMOs. By embracing these trends, PMOs
can become more agile, customer-focused, and value-driven, and play a
key role in driving digital transformation success.
↚
The Role of PMOs in Driving Business Innovation
In the future, Project Management Offices (PMOs) will play a crucial role in driving business innovation. As organizations increasingly rely on innovation to stay competitive, PMOs can provide the structure and support needed to manage innovation projects effectively. Here are some ways PMOs can drive business innovation.
Managing Innovation Projects: Innovation projects often involve
high levels of uncertainty and risk. PMOs can provide a structured
approach to managing these projects, including risk management, resource
allocation, and progress tracking.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation: PMOs can help to foster a
culture of innovation within the organization. This can involve
promoting creative thinking, encouraging risk-taking, and recognizing
and rewarding innovative ideas.
Aligning Innovation with Strategy: PMOs can ensure that
innovation projects are aligned with the organization's strategic
objectives. This can involve prioritizing innovation projects based on
their strategic importance, and ensuring that they deliver value to the
organization.
Providing Tools and Techniques: PMOs can provide tools and
techniques to support innovation, such as project management software,
collaboration tools, and innovation methodologies.
Measuring Innovation Performance: PMOs can track and measure the
performance of innovation projects, using key performance indicators
(KPIs) such as the number of new ideas generated, the success rate of
innovation projects, and the financial impact of innovations.
Facilitating Learning and Improvement: PMOs can facilitate
learning and continuous improvement in innovation projects. This can
involve conducting "lessons learned" sessions, sharing best practices,
and providing training and development in innovation skills.
By playing these roles, PMOs can help organizations to innovate more
effectively and efficiently, leading to improved competitive advantage
and business success.
↚
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
A Project Management Office (PMO) is a crucial component of an organization that aims to standardize project management processes, improve project performance, and ensure alignment of projects with business strategy. Here's a recap of the key points.
PMO Tools and Techniques: PMOs use a variety of tools and
techniques, including project management methodologies, project
management software, and reporting and analytics tools. These tools help
in planning, executing, monitoring, and controlling projects
effectively.
PMO Best Practices: Some of the best practices for PMOs include
aligning projects with business strategy, standardizing project
management processes, providing training and support to project
managers, and focusing on continual improvement and innovation.
Measuring PMO Performance: PMO performance can be measured using
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), PMO Maturity Models, and Benefits
Realization Management. These tools help in assessing the effectiveness
of the PMO and identifying areas for improvement.
Impact of Agile and Digital Transformation: The rise of Agile
methodologies and digital transformation is impacting PMOs, requiring
them to become more agile, flexible, and customer-focused. PMOs need to
adapt their practices and develop new skills to drive digital
transformation success.
Role in Driving Innovation: PMOs can play a key role in driving
business innovation, by managing innovation projects, fostering a
culture of innovation, aligning innovation with strategy, and measuring
innovation performance.
In conclusion, a well-functioning PMO can bring significant
benefits to an organization, including improved project success rates,
better resource utilization, and enhanced alignment of projects with
business strategy. As organizations continue to evolve and face new
challenges, the role of the PMO is likely to become even more important
in the future.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of PMOs
Project Management Offices (PMOs) play a pivotal role in organizations, providing the structure and standardization necessary for managing multiple projects effectively. They serve as a central hub for project management best practices, tools, and methodologies, ensuring consistency across projects and promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
PMOs are instrumental in aligning projects with the organization's
strategic objectives, ensuring that every project contributes to the
overall business goals. They help in prioritizing projects based on
their strategic value, ensuring optimal allocation of resources.
In an era of rapid digital transformation and increasing complexity of
projects, the role of PMOs is becoming even more critical. They are key
drivers in implementing Agile practices, fostering a culture of
innovation, and leading digital transformation initiatives.
Moreover, PMOs play a significant role in risk management,
quality assurance, and benefits realization, ensuring that projects
deliver the expected outcomes and benefits.
In essence, PMOs contribute to enhancing the project management
maturity of an organization, leading to improved project success rates,
better decision-making, and ultimately, enhanced business performance
and competitiveness.
In conclusion, the importance of PMOs cannot be overstated. They are not just administrative bodies, but strategic entities that can drive project success and contribute significantly to the achievement of business objectives.
















💬 شاركنا رأيك أو استفسارك في التعليقات أدناه. مساهمتك تهمنا وتثري النقاش! 👇